Cell membrane:
- partially permeable
- width is 7nm- 7.5nm
- made from a bi- layer of phospholipid molecules in which the hydrocarbon tails are sandwiched to make an inner layer, whereas phosphate heads are lined up on both sides
- larger fraction of the width is hydrophobic, therefore it allows small non- polar particles to pass through while large polar particles are not allowed to pass
- there are special proteins present on the surface or across the width distributed among the phospholipid molecules
- the phosphate heads are hydrophilic and thus compatible with water present inside cytoplasm or outside the cell membrane as tissue fluid
Fluidity of cell membrane~
- is shown by phospholipid molecules which show movement on their axes as well as the proteins scattered along with
- the arrangement of molecules in the call membrane can be represented by Fluid mosaic model
- named because the phospholipid molecules due to their movement along with proteins become fluid part while the Mosaic formation is because of random arrangement of proteins
Fluidity depends on following:
1- length of C-H chain: longer length of tail, lesser fluidity
2- saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon tail: hight the saturation lesser the fluidity
3- a hydrocarbon tail with double bond
4- fluidity is also controlled by the presence of plugging by/ of cholesterol molecules
5- whole cholesterol molecule is hydrophobic except 1 hydroxyl attached to it
6- fluidity can be increased by effect of temperature
Stability of cell membrane~
- phosphate heads being hydrophilic make hydrogen bonds with water around them. this gives the cell membrane stability
- protein present on surface have hydrophilic branches which add on to the stability by making hydrogen bonds with water
- the hydroxyl of cholesterol which is embedded along phosphate heads also gives stability
- the carbohydrate branch of glycoproteins and glycolipids add to the stability of cell membrane by making hydrogen bonds with water outside
[hydrocarbon chain makes up most of the thickness of a cell surface membrane]
Protein in cell membrane~
- there are different kinds of protein which make up cell membrane
can be classified as:
1) intrinsic
2) extrinsic ---> glycolipid
*these are the transmembrane protein present along the whole length of phospholipid molecules
Intrinsic:
- these are found either throughout width of cell membrane
- they can either be present in length of cell membrane or partly along the cell membrane
- most of these proteins are transmembrane proteins
* their function is to help in transport of polar charged particles which cannot pass through phospholipid bi- layer
- there is a channel in the length of protein which can be filled with water allowing polar molecules to pass through, eg: minerals
- channel proteins which allow passage of ions down concentration gradient
- carrier proteins thorough which ions can move against concentration gradient by use of ATP/ energy from respiration
- carrier proteins change either shape on order to left molecules pass through
- these channel and carrier proteins are specific ions
Extrinsic:
- are also known as surface proteins
- can be either enzymes, glycoproteins or lipoproteins
Glycolipids and glycoproteins~ (acts as receptor sites for hormones)
an extrinsic compound made from:
- these molecules can behave as receptors which have following function...
1- for hormone binding
2- antibody formation
3- immune response
- receptors are involved in endocytosis
- for neurotransmitters to attach to neurons
- they are as antigens
- form hydrogen bonds with water
- recognize antibodies
Different kind of transport
Diffusion:
 movement of particles from an area of high concentration to that of lower concentration i.e along concentration gradient e.g, movement of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs through phospholipid layers due to their small size. other non- polar molecules also show some kind of movement
movement of particles from an area of high concentration to that of lower concentration i.e along concentration gradient e.g, movement of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs through phospholipid layers due to their small size. other non- polar molecules also show some kind of movementDiffusion can be facilitated if it is of charged particles like ions and it is possible only through specific channel proteins

~Fraction affecting rate of diffusion:
- concentration gradient: higher the concentration gradient, faster the diffusion
- surface area: higher the surface area, higher the rate of diffusion
- temperature: about kinetic energy of molecules higher temperature, higher rate of diffusion
- size: smaller the size, greater the rate
For facilitated diffusion surface area would only matter with an increase of transfer. facilitated diffusion is limited by the number of protein channel in the membrane
Active transport:
 movement of polar molecules against the concentration gradient from lower to higher concentration with use of energy from ATP molecules. It happens through carrier proteins
movement of polar molecules against the concentration gradient from lower to higher concentration with use of energy from ATP molecules. It happens through carrier proteinsWhy is energy needed for active transport?
it takes place when a specific carrier protein changes its structure temporarily when an ion comes close to it. this change in 3D structure needs energy
ATP isn't a result of random movement of molecules whereas simple and facilitated diffusion is
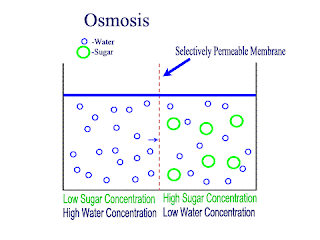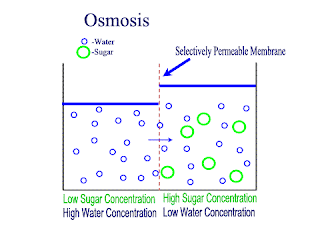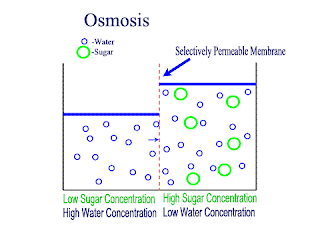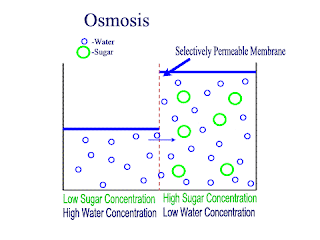
Osmosis:
net movement of water molecule from higher water potential to lower water potential across partially permeable membrane
Water potential: ability of a solution to give away free water molecules. a dilute solution has higher water potential than a concentrated solution. distilled water has the higher water potential of zero. water potential of a solution is a negative value
Solute potential: it is the ability of the solute in the solution to lower the water potential
*a concentrated solution which has low water potential also has lower solute potential. whereas a dilute solution which has a high water potential will have a higher solute potential
higher solute potential= less negative value
lower solute potential= more negative value
For plant cells:
Ψ=Ψs+Ψp
(-) (+)
Incipient plasmolysis: 1st stage when a plant cell starts to shrink so that there is no more pressure on the cell wall
Bulk transport~
when solids or liquids pass across the cell membrane in bulk e.g, endocytosis.
It is the process by which large particles pass from outside to inside the cell e.g, phagocytosis
Phagocytosis: (endocytosis)
Step 1: a bacterium attaches itself on the receptor (glycoprotein) of a phagocyte
step 2: a depression form in the plasma membrane surrounding the bacteria
step 3: a vesicle is formed called phagocytosis vesicle. a golgi vesicle buds off containing lysozymes thus forms a lysosome
step 4: this lysosome then moves toward the phagocytic vesicle and then fuses with it to form secondary vesicle
step 5: the bacteria then gets digested by hydrolytic enzymes and the debris is taken. the debris of the bacterium is taken to cell membrane through excretory vesicle
 Endocytosis: the movement of solids in bulk from inside to outside the cell
Endocytosis: the movement of solids in bulk from inside to outside the cell*when something has to move out, it comes close to the plasma membrane through a vesicle which then fuses with the membrane passing the contents out of the cell
* Exocytosis can be through a secretory or an excretory vesicle
 Pinocytosis: cell drinking
Pinocytosis: cell drinking- many small vesicle carry liquid in through the plasma membrane



Awesome blog. I enjoyed reading your articles. This is truly a great read for me. I have bookmarked it and I am looking forward to reading new articles. Keep up the good work! tenda membrane
ReplyDeleteHello I am so delighted I located your blog, I really located you by mistake, while I was watching on google for something else, Anyways I am here now and could just like to say thank for a tremendous post and a all round entertaining website. Please do keep up the great work. Epiretinal Membrane
ReplyDeleteMy Silver Service provides premium service and luxury cars at cheap rates to all customers and clients.
ReplyDeleteSilver Service Taxis Geelong
Amazing notes, left nothing out; Could work on the grammar and sentences tho some were a bit difficult to get, but it was a great help overall!
ReplyDeleteNice Blog. Thanks for sharing with us. Such amazing information.
ReplyDeleteTop Boarding School in Dehradun
Top Boarding School in India
Best Boarding School in Uttarakhand
Top Residential School in Dehradun
Top Boarding School in India Fee Structure
Top Coed Boarding School in India